This 4th of July morning was gray with the clouds of an impending storm. We went to check out a heron nest I saw a couple of weeks ago. And it was so great to look over there and see all these great tall birds perched in their aerie! At first they were bunched together so it was hard to see how many there were.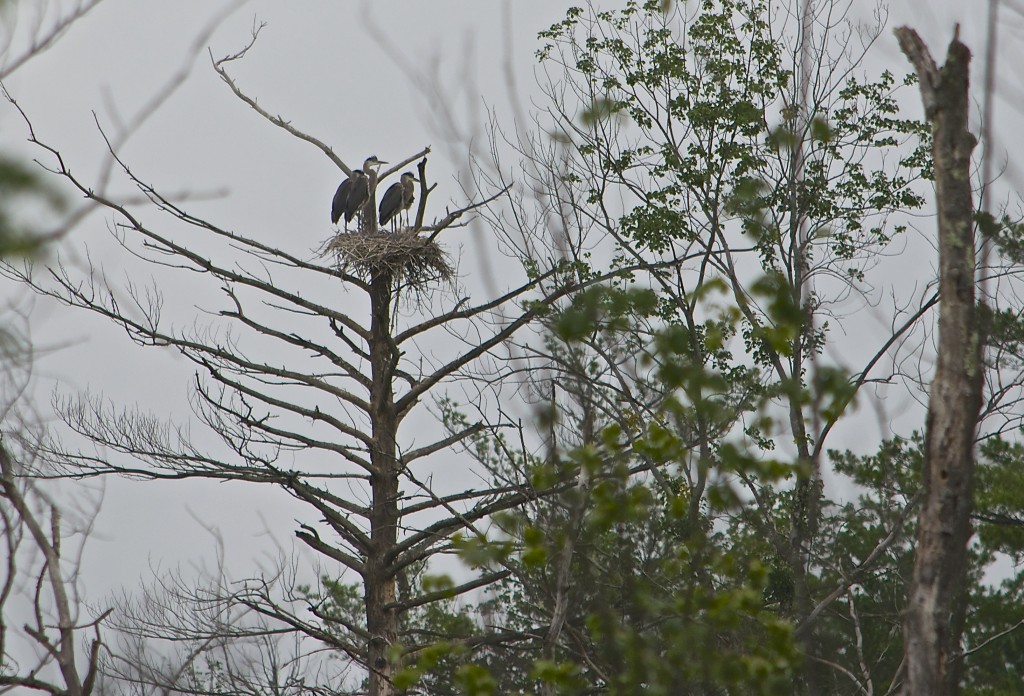 
But then they wandered around a bit, revealing four.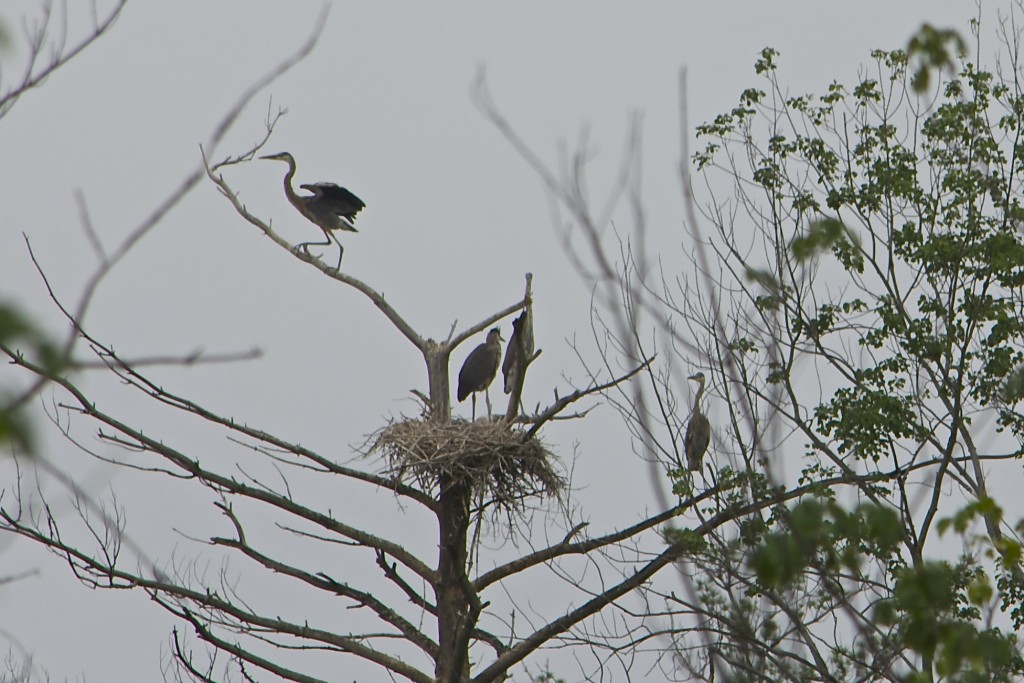
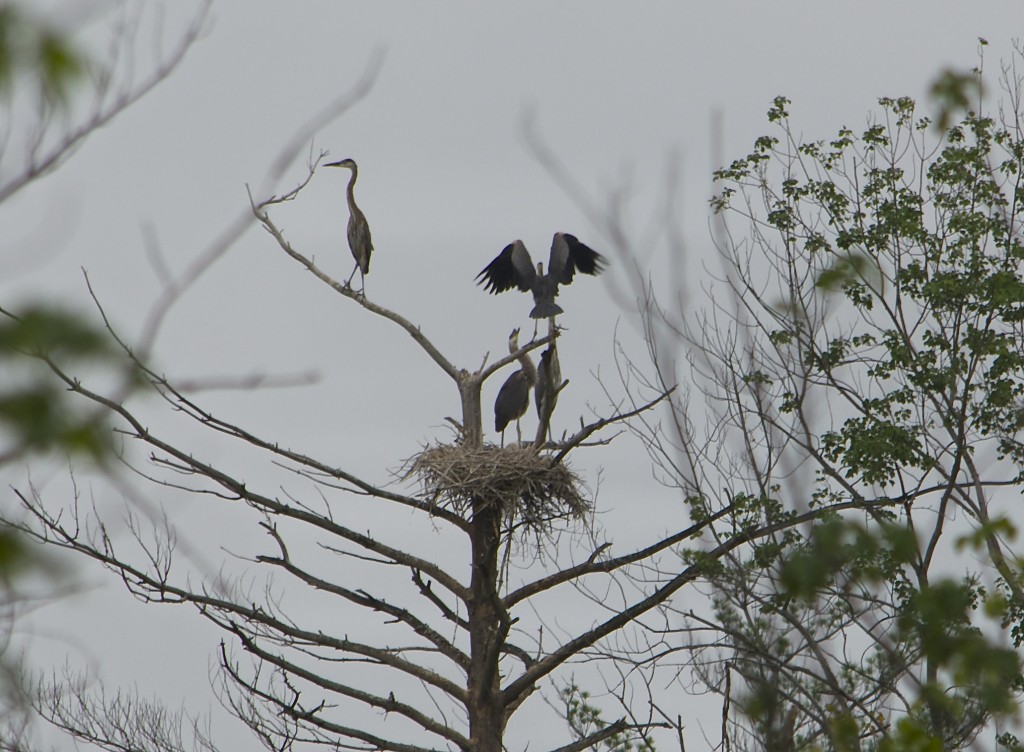

I hope they come through this storm okay (remnants of Hurricane Arthur). Glad there is enough habitat here to support them. Imagine building that nest (with your mouth) — how do you get the first sticks to stay? Clever birds!
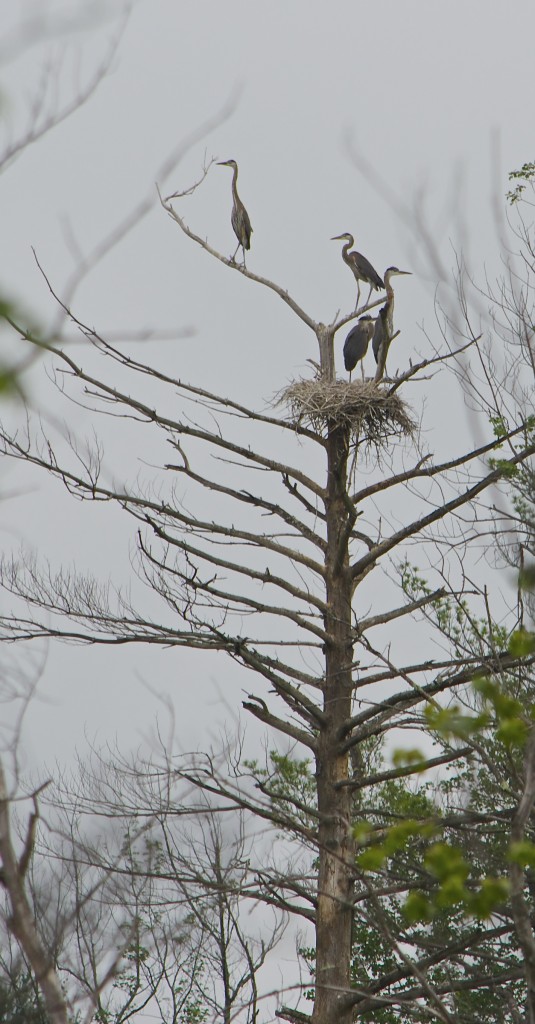

Great Blue Herons will eat just about anything they can catch, including fish, insects, mammals, amphibians, reptiles and even birds. They can hunt during the day and night, because of good night vision. We’ve noticed new beaver dams in our favorite hiking areas, and this is a boon for herons because hunting is good in the swamps created by the dams.
From allaboutbirds.org:
Male Great Blue Herons collect much of the nest material, gathering sticks from the ground and nearby shrubs and trees, and from unguarded and abandoned nests, and presenting them to the female. She weaves a platform and a saucer-shaped nest cup, lining it with pine needles, moss, reeds, dry grass, mangrove leaves, or small twigs. Nest building can take from 3 days up to 2 weeks; the finished nest can range from a simple platform measuring 20 inches across to more elaborate structures used over multiple years, reaching 4 feet across and nearly 3.5 feet deep. Ground-nesting herons use vegetation such as salt grass to form the nest.
Great Blue Herons nest mainly in trees, but will also nest on the ground, on bushes, in mangroves, and on structures such as duck blinds, channel markers, or artificial nest platforms. Males arrive at the colony and settle on nest sites; from there, they court passing females. Colonies can consist of 500 or more individual nests, with multiple nests per tree built 100 or more feet off the ground.
— A clutch will have 2-6 eggs, which are about 2.5 to 3 inches long. They incubate for about a month, and the young stay in the nest 4 to 7 weeks. These ones must be about ready to strike out on their own. Pairs choose new breeding partners each year.
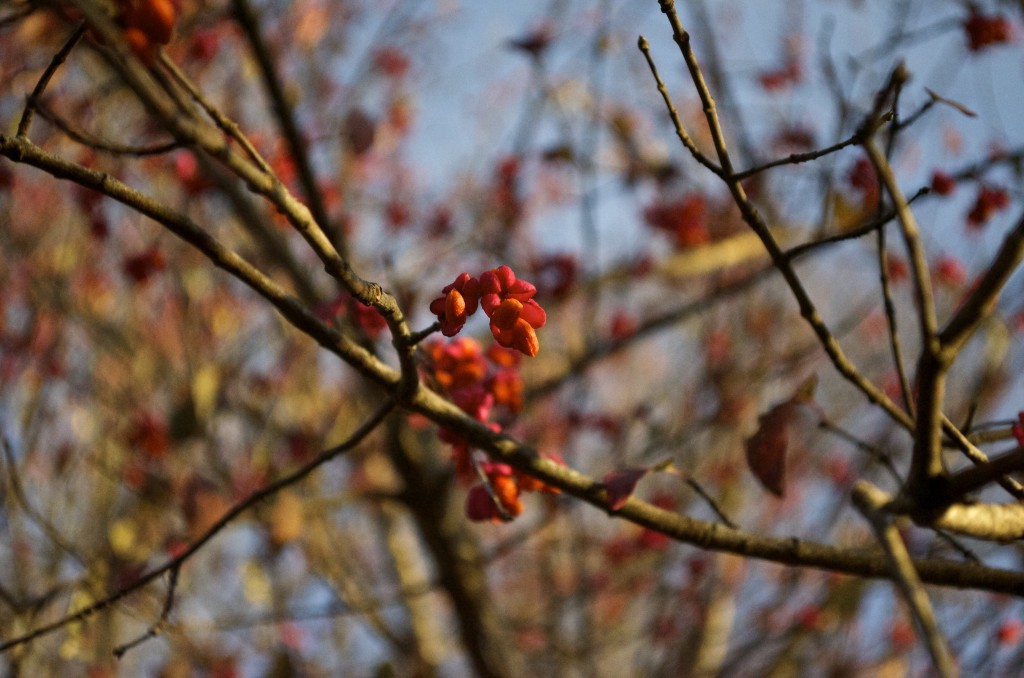 All the wildflowers have gone to fruit and seeds. This shot is from November 19. Wahoo is a Dakota term for this plant, which means “arrow wood.” Native to North America, related to bittersweet and also to the non-native invasive kind of euonymous.
All the wildflowers have gone to fruit and seeds. This shot is from November 19. Wahoo is a Dakota term for this plant, which means “arrow wood.” Native to North America, related to bittersweet and also to the non-native invasive kind of euonymous.
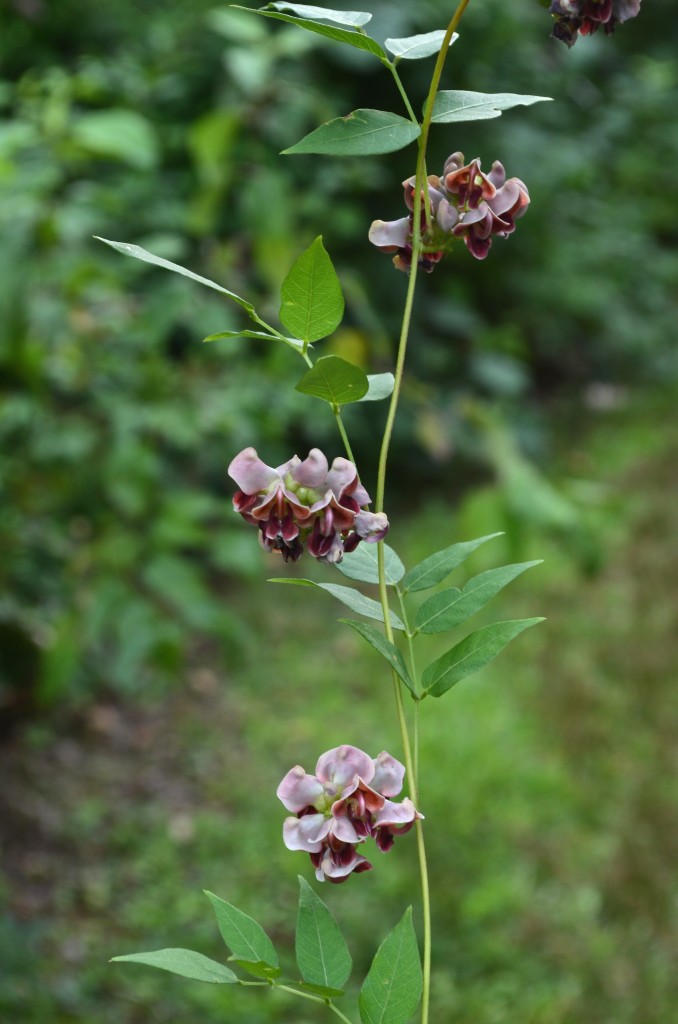
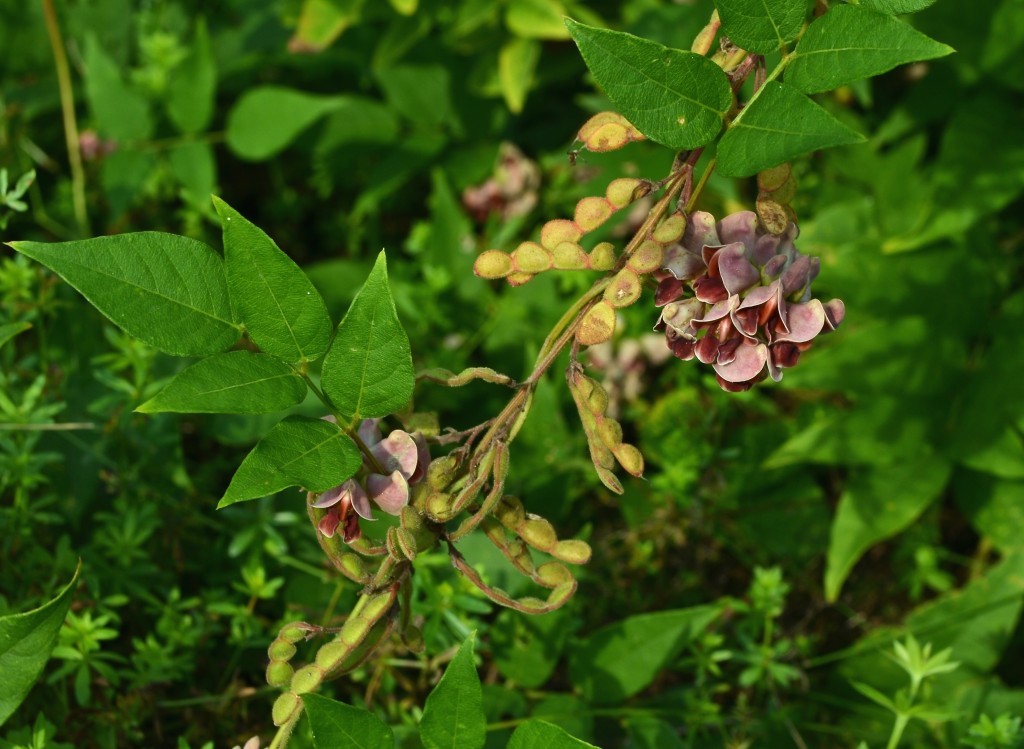
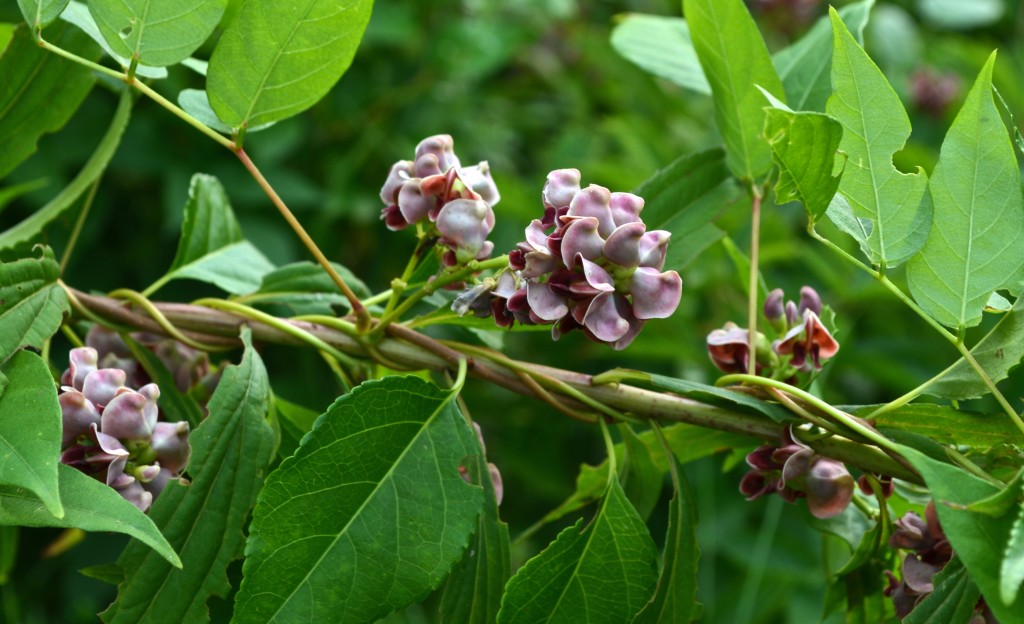
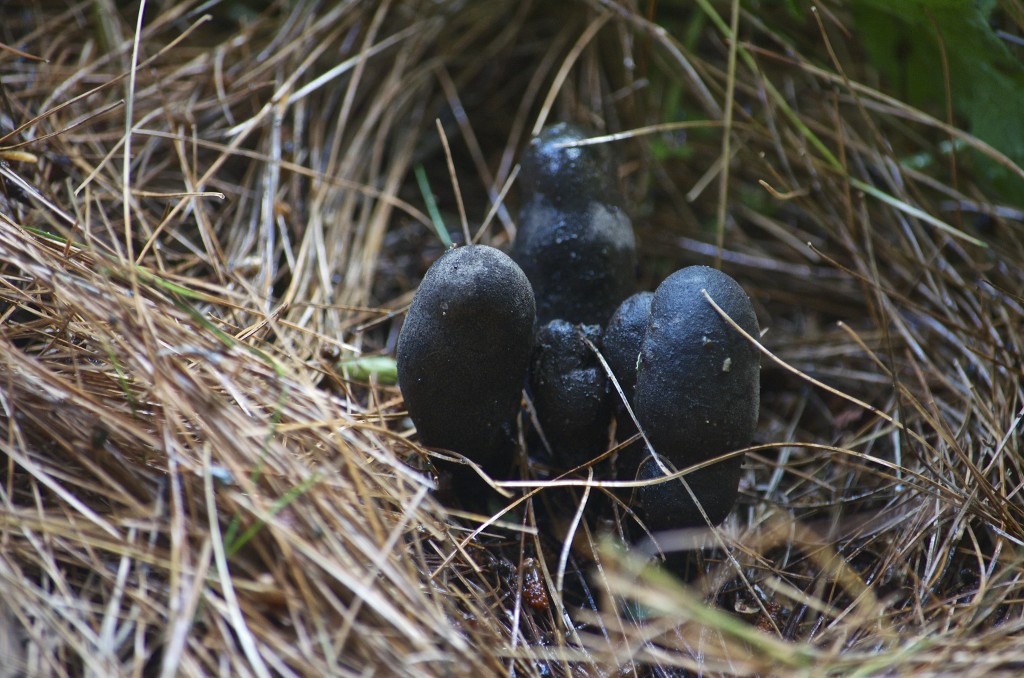
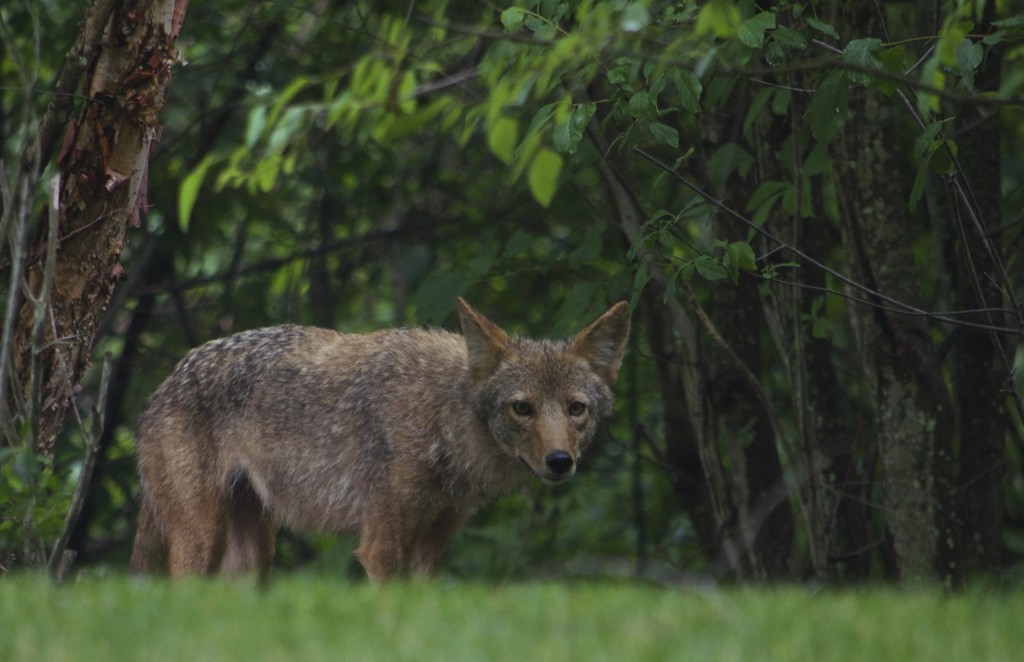
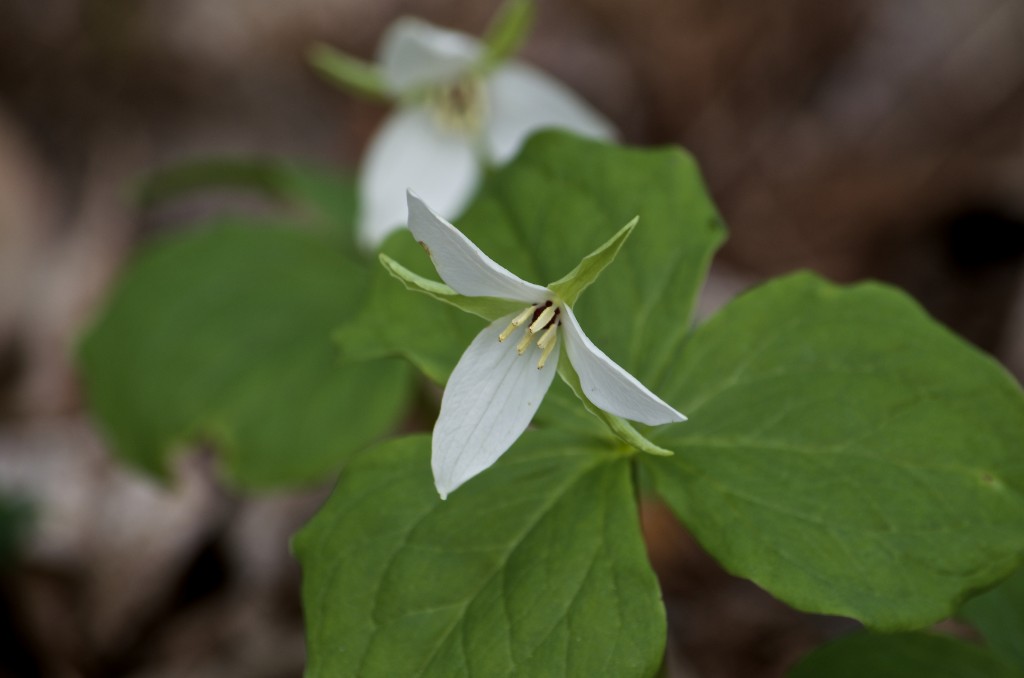
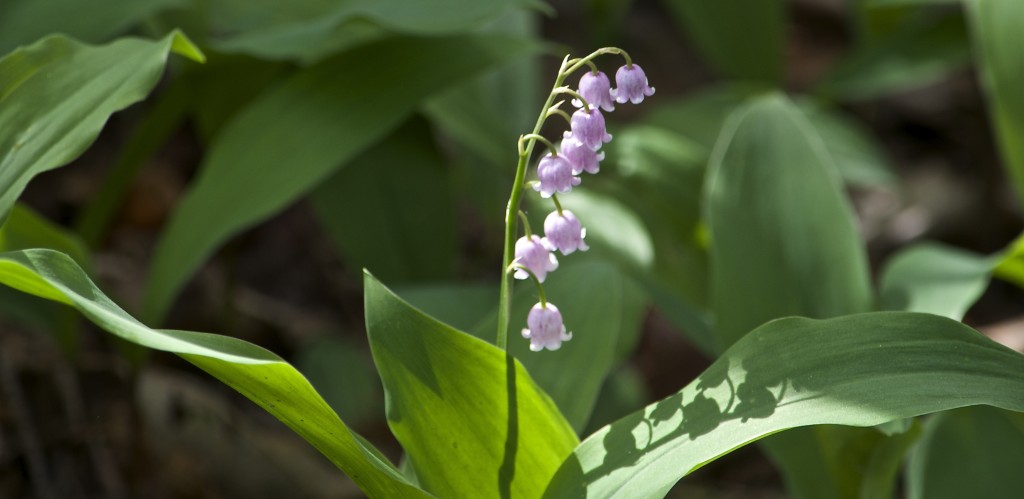
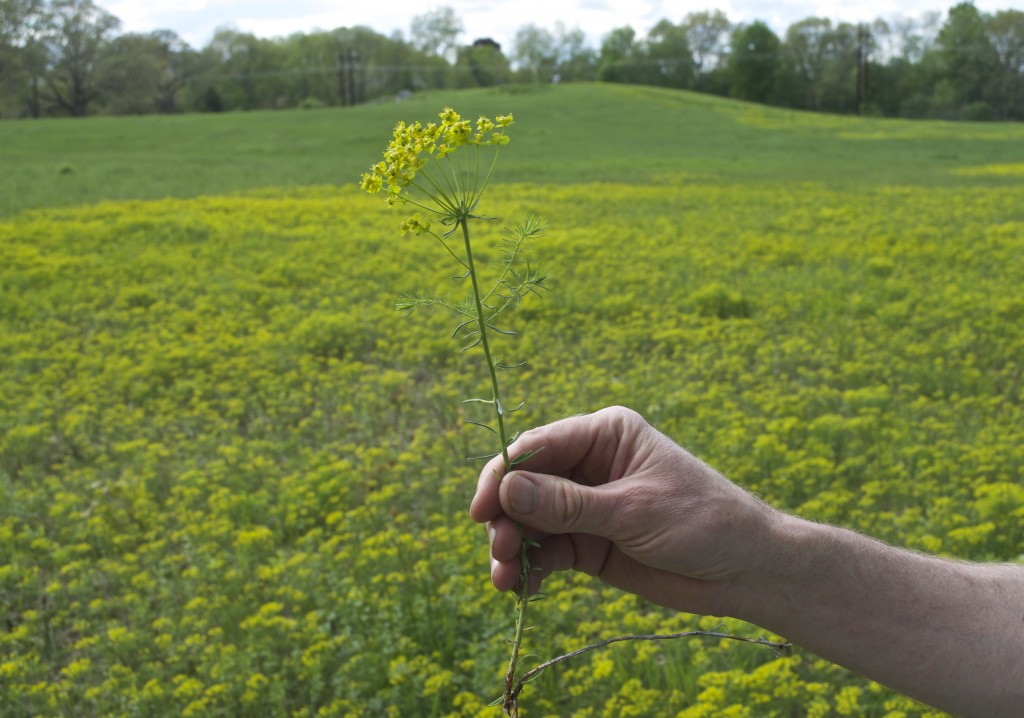
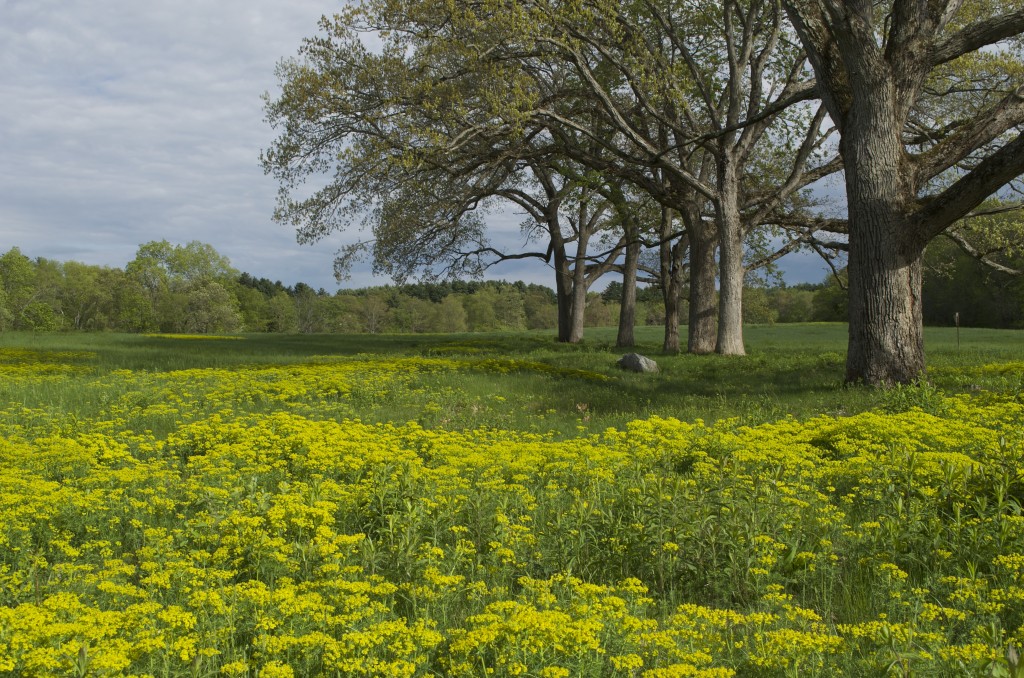
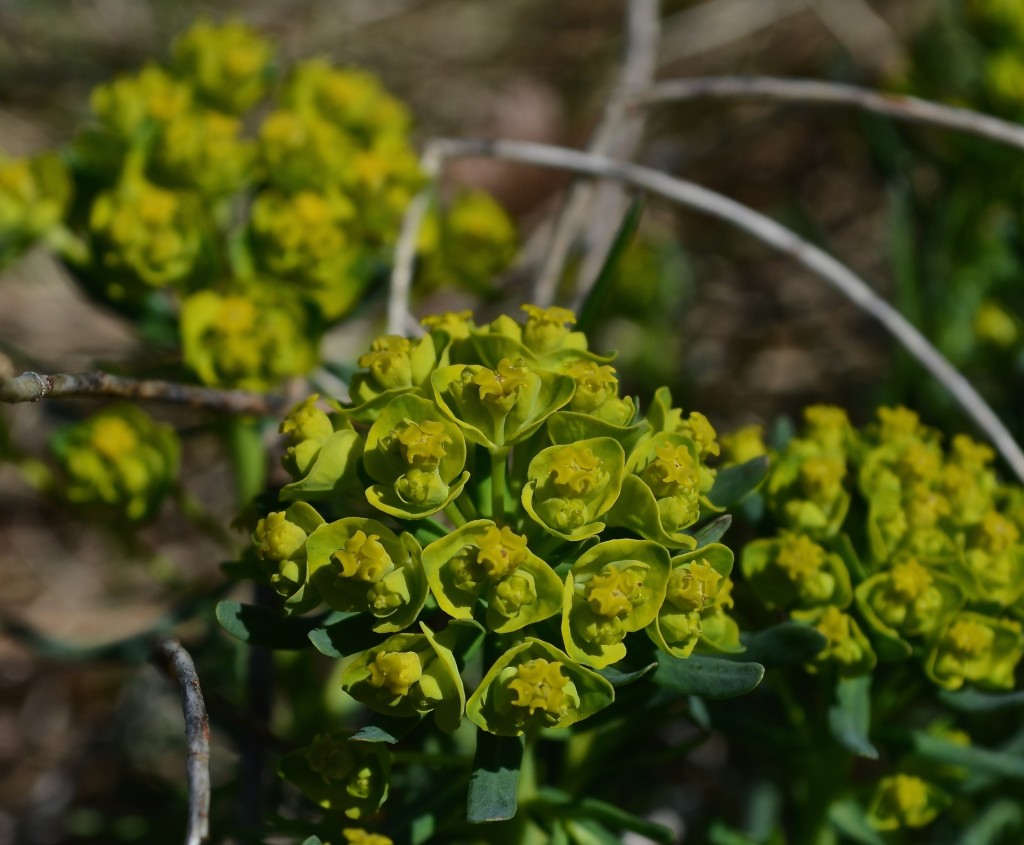


















 A hardy groundcover — tolerates poor soil, dry conditions, deer, rabbits, pollution… Has a milky, poisonous sap that repels herbivores. Forms a dense fluffy blanket about a foot tall. Tiny flowers that start lime-green and yellow, and age to red. Has narrow-leaved foliage reminiscent of cypress trees, hence the name cypress spurge. (The common name “spurge” comes from the Middle English/Old French word “epurge”, meaning “to purge”, because these plants were used as purgatives. (Poinsettias are spurges!) Native to Europe, introduced to North America in the 1860s as an ornamental, and is now a harmful invasive that has really colonized Charles River Peninsula.
A hardy groundcover — tolerates poor soil, dry conditions, deer, rabbits, pollution… Has a milky, poisonous sap that repels herbivores. Forms a dense fluffy blanket about a foot tall. Tiny flowers that start lime-green and yellow, and age to red. Has narrow-leaved foliage reminiscent of cypress trees, hence the name cypress spurge. (The common name “spurge” comes from the Middle English/Old French word “epurge”, meaning “to purge”, because these plants were used as purgatives. (Poinsettias are spurges!) Native to Europe, introduced to North America in the 1860s as an ornamental, and is now a harmful invasive that has really colonized Charles River Peninsula.